Simulation
Contents
Simulation#
Packages#
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import ams_functions as ams
Using the Model solution#
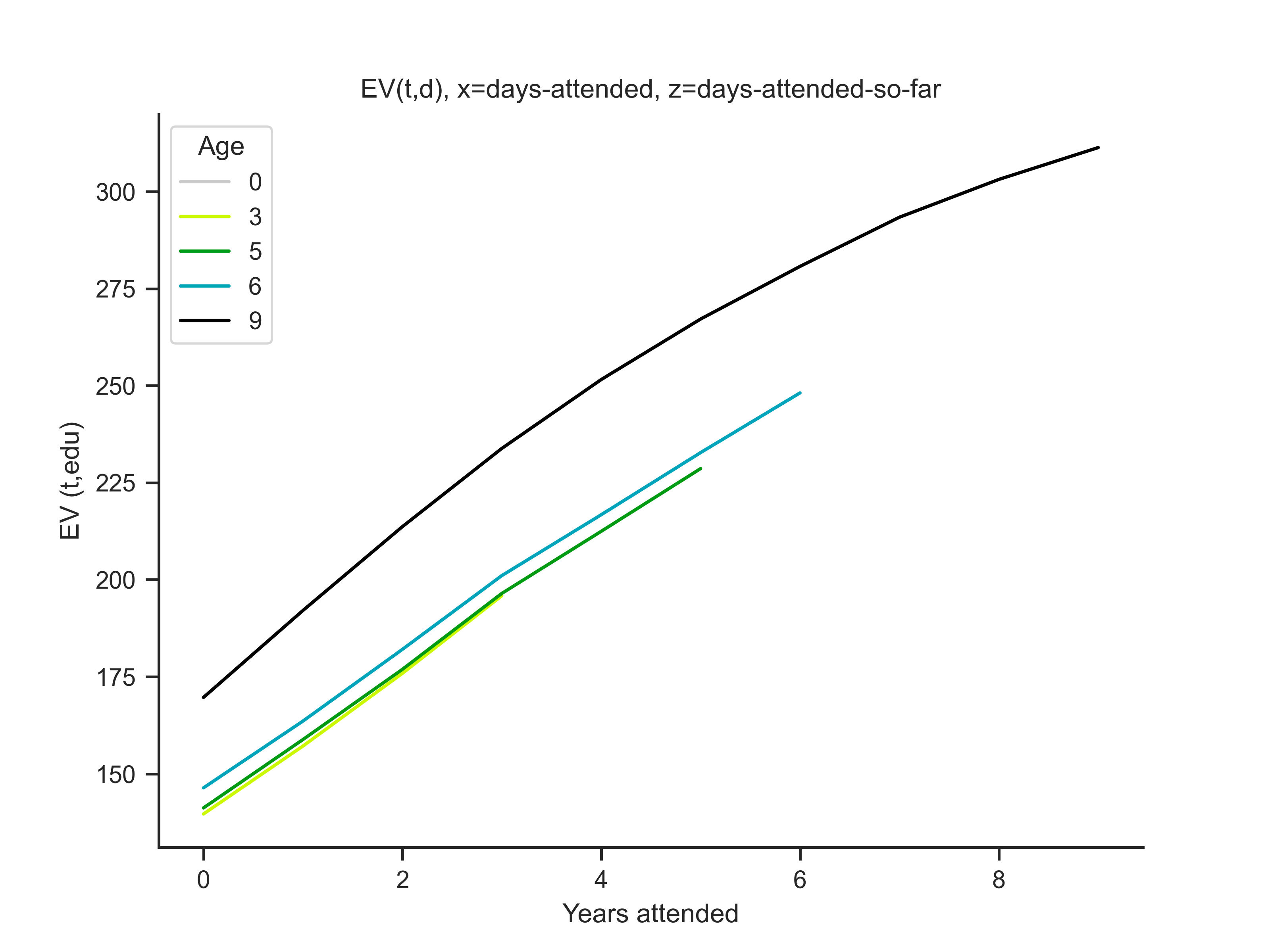
Using the model solution we can get the expected value matrix to use in our simulation. We will use this to calculate the utility for working and going to school.
probs_w, probs_s, eps_t, eve_w, eve_s, vf = ams.solution()
Simulation#
Parameters#
We need to define how many individuals we are going to simulate and other parameters for our simulation. The parameters are:
Shock mean (
ϵ_mean)Shock Standart deviation (
ϵ_sd)The age that we start simulating children choices (
age_start)The maximum additional years to
age_start. In our case we willage_start+age_max= 15, 15 is the last year that we are going to simulate.Number of individual (
sim)Discount factor (
β)
About the shock, we are considering a logistic distribution.
np.random.seed(1996)
ϵ_mean = 0
ϵ_sd = 1
age_start = 6
age_max = 10
sim = 100
β = 0.9
Creating Matrices#
Now, we need to create the matrices to store our results and create a dataframe with our individual. We will store the following:
Schooling decision
Education Level in the current period
Education Level in the next period
Age of the child
Shock received
Utility obtained from decision
Consumption obtained from decision
# School decision
S_dec = np.empty((age_max,sim))
S_dec[:] = np.nan
# Education level (current period)
ed_cur = np.empty((age_max,sim))
ed_cur[:] = np.nan
# Education level (next period)
ed_next = np.empty((age_max,sim))
ed_next[:] = np.nan
# Age
age_c = np.empty((age_max,sim))
age_c[:] = np.nan
# Shock
eps = np.empty((age_max,sim))
eps[:] = np.nan
# Utility
U = np.empty((age_max,sim))
U[:] = np.nan
# Comsumption
C = np.empty((age_max,sim))
C[:] = np.nan
Simulating the individuals#
Now we will loop our simulated individuals using the vf matrix obtained using the model solution code. The loop is commented in order to understand the steps.
# Loop to simulate the individuals
for s in range(sim):
# All the individuals start with no education
edu = 0
for age in range(age_max):
# Actual child's age
age_c[age,s] = age_start + age
ed_cur[age,s] = edu
# Random shock to education cost
e_shock = np.random.logistic(loc = ϵ_mean, scale = ϵ_sd)
# Random shock to primary education sucess
e_sucess = np.random.uniform()
if age == age_max - 1:
s_ev = ams.prob_progress(edu)*ams.terminal_v(edu=edu+1) + (1 - ams.prob_progress(edu))*ams.terminal_v(edu=edu)
w_ev = ams.terminal_v(edu=edu)
else:
s_ev = ams.prob_progress(edu)*vf[age+1, edu+1] + (1 - ams.prob_progress(edu))*vf[age+1,edu]
w_ev = vf[age+1, edu]
# Utility for choices
school = ams.utility(age, edu, school=1, ϵ = e_shock) + β*s_ev
work = ams.utility(age, edu, school=0, ϵ = e_shock) + β*w_ev
# Decision that max utility for individual
dec = max(school, work)
u = dec
if u == school:
if e_sucess <= ams.prob_progress(edu):
suc = 1
else:
suc = 0
ed_next[age,s] = edu + suc
C[age,s] = ams.budget_constraint(age, edu, school=1)
U[age,s] = dec
S_dec[age,s] = 1
else:
suc = 0
ed_next[age,s] = edu + suc
C[age,s] = ams.budget_constraint(age, edu, school=0)
U[age,s] = dec
S_dec[age,s] = 0
eps[age,s] = e_shock
edu = edu + suc
Now we can use the data created to build our dataframe.
simulated_data = []
for i in range(sim):
s = {}
s['id'] = i
s['age'] = list(range(6,16))
s['edu'] = list(ed_cur[:,i])
s['edu_next'] = list(ed_next[:,i])
s['School'] = list(S_dec[:,i])
s['eps'] = list(eps[:,i])
s['U'] = list(U[:,i])
s['C'] = list(C[:,i])
s = pd.DataFrame(s)
simulated_data.append(s)
simulated_data = pd.concat(simulated_data, axis = 0).reset_index().drop('index', axis = 1)
print(simulated_data)
id age edu edu_next School eps U C
0 0 6 0.0 1.0 1.0 0.486600 157.077295 0.000000
1 0 7 1.0 2.0 1.0 -0.231324 167.333910 0.000000
2 0 8 2.0 3.0 1.0 -2.649542 178.663684 0.000000
3 0 9 3.0 4.0 1.0 0.168511 198.323842 30.958571
4 0 10 4.0 4.0 1.0 1.114490 214.442327 35.721429
.. .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
995 99 11 5.0 6.0 1.0 -0.958147 229.973267 45.247143
996 99 12 6.0 7.0 1.0 2.979259 253.427881 61.917143
997 99 13 7.0 7.0 1.0 -0.624382 270.277544 95.257143
998 99 14 7.0 8.0 1.0 -0.273750 281.102625 95.257143
999 99 15 8.0 9.0 1.0 1.556712 307.177538 104.782857
[1000 rows x 8 columns]
We also can replicate this using the function from the ams_functions file, ams.simulation(), wich is this routine collapsed in the function.
sim = ams.simulation()
print(sim)
id age edu edu_next School eps U C
0 0 6 0.0 0.0 1.0 1.812244 158.402939 0.000000
1 0 7 0.0 1.0 1.0 -0.679639 149.017691 0.000000
2 0 8 1.0 2.0 1.0 0.887517 163.325623 0.000000
3 0 9 2.0 3.0 1.0 0.612907 178.760986 0.000000
4 0 10 3.0 4.0 1.0 -1.030982 196.138880 30.958571
.. .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
995 99 11 5.0 6.0 1.0 -0.142327 230.789088 45.247143
996 99 12 6.0 7.0 1.0 -0.152864 250.295757 61.917143
997 99 13 7.0 8.0 1.0 0.913260 271.815187 95.257143
998 99 14 8.0 9.0 1.0 -0.733853 290.638434 104.782857
999 99 15 9.0 10.0 1.0 -2.864081 310.904298 114.308571
[1000 rows x 8 columns]
You can see that the dataframes are equal.
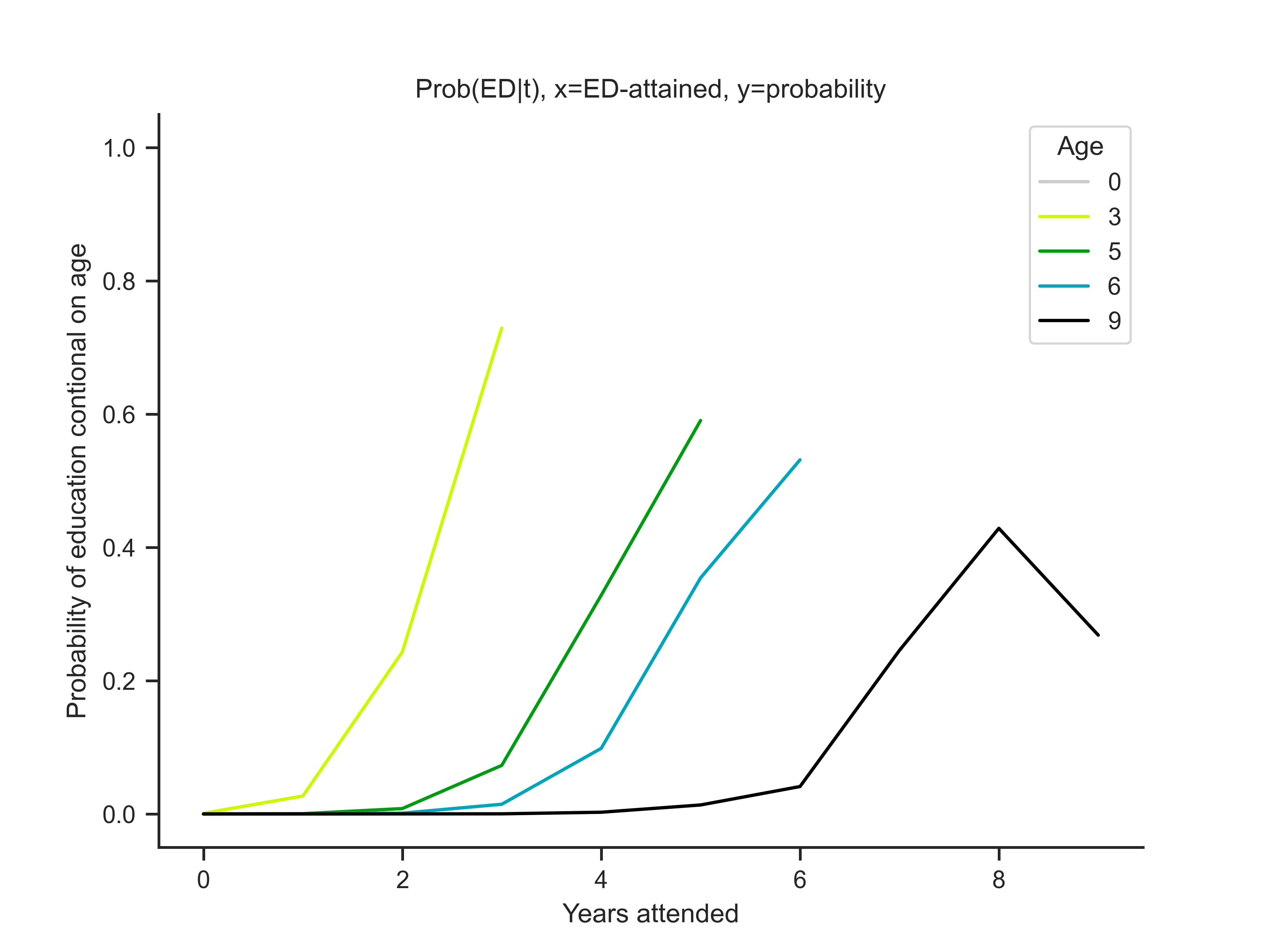
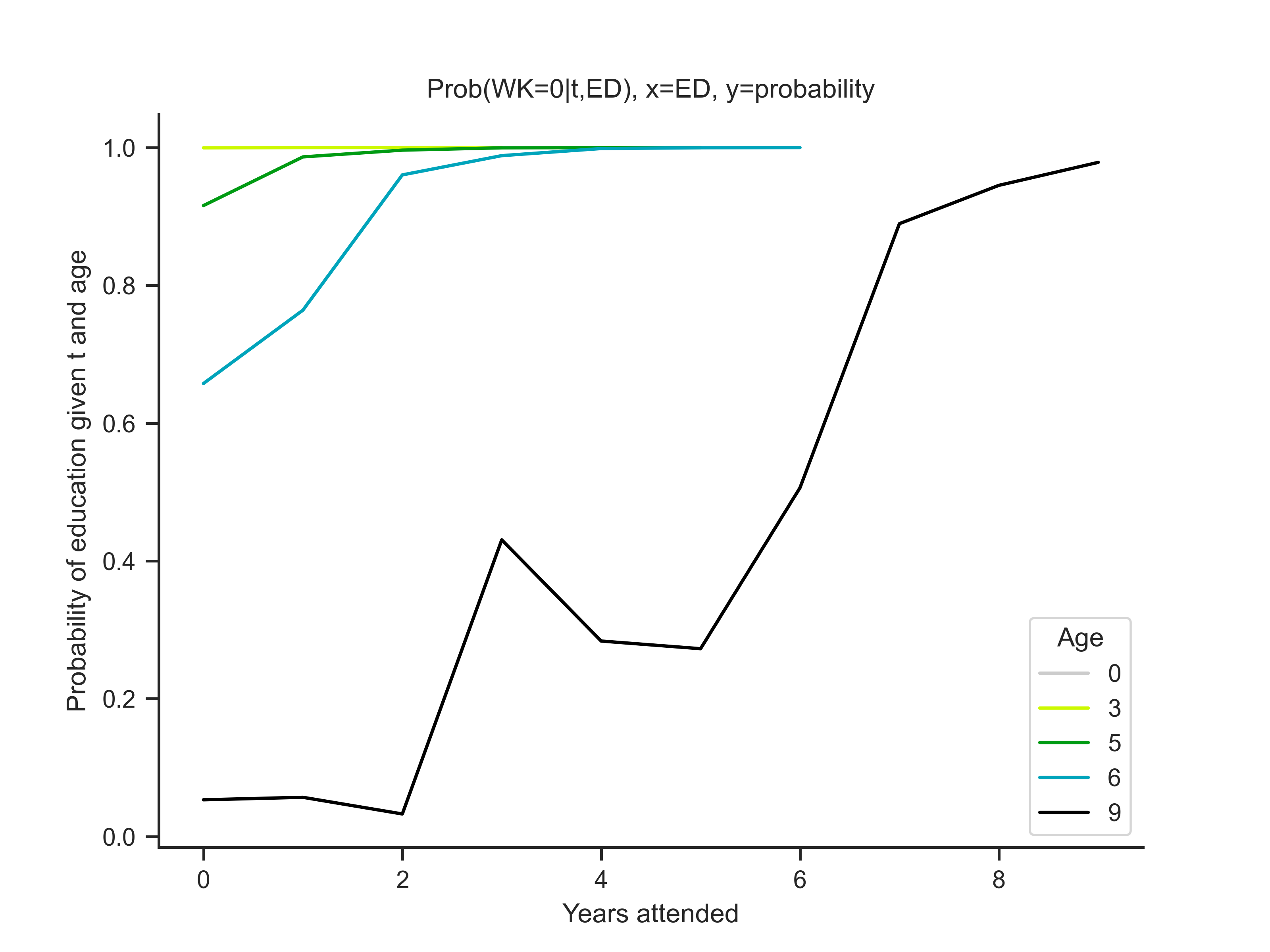
Probabilities matrices#
Now we will simulate the probabilities based on our simulated data
probs_s = ams.solution()[1]
prob_sim = np.zeros((age_max,age_max))
prob_sim[0,0] = 1 # Everybody is the same in the begining
for age in range(1,age_max):
for edu in range(age):
prob_mass = prob_sim[age-1,edu] # Mass of students in age 0 and with edu 1
prob_s_age_edu = probs_s[age-1,edu] # P(L = 0 | t = t-1, d = d)
if np.isnan(prob_s_age_edu): # Maybe is not possible, but I defined as nan in the model solution
prob_s_age_edu = 0
else:
pass
prob_sim[age,edu] = prob_sim[age,edu] + (1-prob_s_age_edu)*prob_mass + \
((1 - ams.prob_progress(edu))*prob_s_age_edu)*prob_mass # Adding the 0 to the teachers proportion multiplied by the conditional prob to leisure
prob_sim[age,edu+1] = prob_sim[age,edu+1] + (ams.prob_progress(edu)*prob_s_age_edu)*prob_mass # Same as (214) but now with prob to work
Use a function to calculate discrete probabilities
prob_sim = ams.discrete_probs()
print(prob_sim)
[[1.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00
0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00
0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00]
[1.00000066e-01 8.99999934e-01 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00
0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00
0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00]
[1.00001110e-02 1.80000102e-01 8.09999787e-01 0.00000000e+00
0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00
0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00]
[1.00019368e-03 2.70004262e-02 2.42999903e-01 7.28999477e-01
0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00
0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00]
[1.00354846e-04 3.60126474e-03 4.86006713e-02 2.91598849e-01
6.56098860e-01 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00
0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00]
[1.04090611e-05 4.53938035e-04 8.10392099e-03 7.28986030e-02
3.28046228e-01 5.90486900e-01 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00
0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00]
[1.82958733e-06 5.95118222e-05 1.24075146e-03 1.45804498e-02
9.84079051e-02 3.54278094e-01 5.31431458e-01 0.00000000e+00
0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00]
[7.46853746e-07 1.96765498e-05 2.09304680e-04 2.68436462e-03
2.29358896e-02 1.23945793e-01 3.71941004e-01 4.78263221e-01
0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00]
[5.24250772e-07 1.29009241e-05 1.11497593e-04 5.71018664e-04
5.68416388e-03 3.25452241e-02 1.48419947e-01 4.54058688e-01
3.58596035e-01 0.00000000e+00]
[4.60830022e-07 1.11206781e-05 1.01415775e-04 2.04580307e-04
2.59056039e-03 1.35006688e-02 4.11551927e-02 2.45432603e-01
4.28644222e-01 2.68359176e-01]]
Now we will plot the simulation results
ams.t_graphs()